Technological Barriers in Communication
Do you ever wonder why, despite all the amazing tools available, clear communication still feels so difficult? Technology in communication was supposed to make life easier. We all have smartphones, use instant messaging, and jump on video calls at work or with family. Yet, people often face unexpected obstacles that disrupt the flow of communication, causing frustration and misunderstandings.
So, what causes these problems? Why do organizations and individuals struggle to get their message across, even with advanced technology? And most importantly, how can you overcome technological barriers in communication to make information exchange smoother, whether you’re at home, work, or anywhere else?
What Are Technological Barriers to Communication?
Technological barriers in communication refer to any obstacles that make it difficult for people to share information, ideas, or feelings due to limitations in digital tools, infrastructure, or skills. These barriers can pop up in many different settings, from business meetings to virtual classrooms, even in healthcare and social care organizations.
The rapid adoption of information and communications technology means more people rely on devices and digital platforms for everything—work, education, and personal relationships. But when internet access is unreliable, software systems are incompatible, or privacy concerns arise, it creates real problems. For example, a video call can get interrupted by poor internet connectivity, leading to misunderstandings. Or, an organization might use outdated hardware that can’t run new communication tools, making it difficult for employees to participate fully.
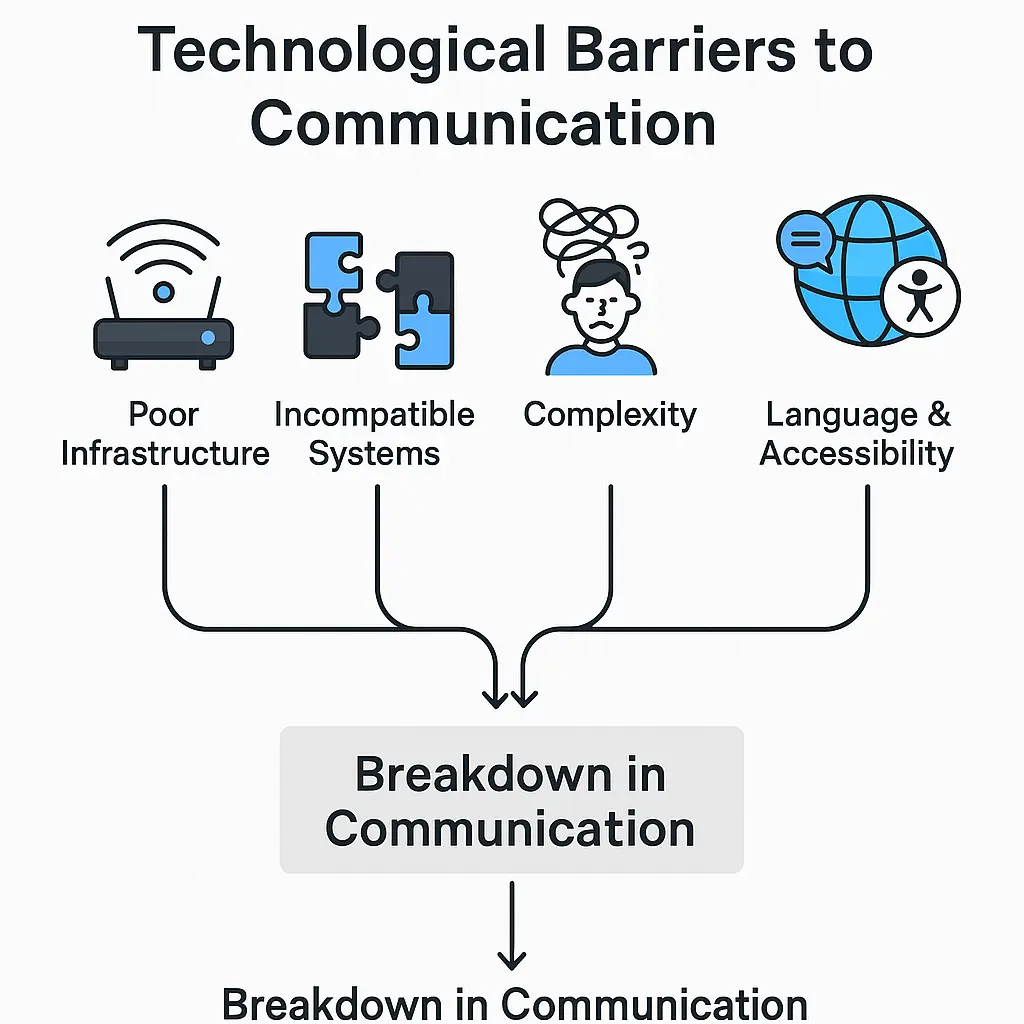
Some of the most common technological barriers include:
- Poor infrastructure (slow or unstable internet, outdated hardware)
- Complexity of communication tools and software applications
- Digital divide—unequal access to modern technology between regions or social groups
- Incompatibility between different platforms or software systems
- Lack of user training or confidence with new tools
- Security risks like data breaches or privacy concerns
Understanding these challenges is the first step to overcoming technological obstacles and ensuring effective communication in every environment.
Types of Technological Barriers in Communication
There’s no single cause for communication problems in the digital age. Instead, a mix of factors can disrupt how information flows within organizations and among individuals.
Infrastructure and Internet Access
Reliable internet access is the backbone of digital communication. Unfortunately, not everyone has the same quality of connectivity. Inadequate infrastructure leads to dropped calls, slow downloads, and laggy video conferences. This is especially true in rural areas, developing countries, or aging buildings that lack modern computer hardware.
For example, virtual teams in Canada may struggle to coordinate if some members have limited internet access. Even in large cities, poor Wi-Fi or outdated routers can disrupt the flow of communication, making collaboration harder.
Incompatibility and Outdated Technology
Not all organizations upgrade their software or hardware regularly. Outdated tools or incompatible systems can block the smooth exchange of information. Imagine trying to share files between a new computer and an old legacy system. Or, consider the challenge of running modern video conferencing apps on a device with outdated software.
In healthcare, for example, electronic health records often need to interact with other digital platforms. If these systems don’t “talk” to each other, it can hinder effective communication between health professionals and unlicensed assistive personnel, affecting patient care.
Complexity and Usability Issues
Some communication platforms or devices are simply too complex for everyday users. Confusing user interfaces, too many features, or poor instructions can discourage participation. People may avoid using certain communication tools effectively if they find them overwhelming.
User experience is crucial. An intuitive interface (computing) encourages adoption, while a confusing layout can frustrate users and lead to errors. This is especially true for the elderly, people with disabilities, or those who lack formal digital education.
Security Risks and Privacy Concerns
Privacy is a growing concern. When sensitive information is shared online, the risk of data breaches or unauthorized access increases. This can make people hesitant to use digital communication channels, especially when handling confidential data.
Information security audit processes are important in business and healthcare to protect personal data. However, strict security measures can also slow down communication or prevent the use of convenient digital platforms.
Language and Cultural Barriers
Technology can magnify language and cultural differences. Automated translation tools are helpful but not perfect. Misinterpretation and misunderstanding can occur due to language barriers or cultural nuances, especially in global organizations or virtual teams.
Even when using digital tools, communication can lead to frustration if the software or application does not support multiple languages or accessible features for people with disabilities or dementia.
Real-World Examples of Technological Barriers
Sometimes it’s easier to understand these barriers with real-life scenarios:
- A nursing home uses an outdated computer system for patient records. The legacy system can’t connect with newer electronic health record software, leading to confusion among staff and health professionals.
- Virtual teams in international organizations experience miscommunication during online meetings due to poor internet connectivity or incompatible video call platforms.
- Elderly care providers may avoid digital communication tools if the interface is too complex or not adapted for ageing users, affecting the quality of self-care and long-term care coordination.
- Unreliable email systems lead to information overload, making it hard for staff to find urgent messages among less important notifications.
These examples highlight that technological barriers refer to more than just broken devices—they involve a complex mix of infrastructure, software, human skills, and even organizational culture.
Causes of Technological Barriers
So, why do these barriers occur in the first place? The root causes are usually linked to access, skills, and compatibility.
- Limited access to modern technology means some people or organizations are left behind, unable to use communication tools effectively.
- Complexity of new devices or software discourages people from adopting them, leading to reliance on outdated tools.
- Incompatibility between systems, platforms, or software versions can hinder communication, especially when different departments or organizations need to share data.
- Privacy and security concerns create reluctance to use digital channels for sensitive or important information.
- Information overload happens when people receive too much data, often through email or instant messaging, making it difficult to focus on important messages.
In each case, the ability to communicate effectively is affected by a combination of technical and human factors.
The Impact of Technological Barriers on Organizations
For any organization, whether in business, education, or healthcare, technological barriers disrupt workflows and make teamwork harder. Poor communication can lead to mistakes, missed deadlines, and lower morale.
- Business: Slow internet, incompatible communication devices, or complex software systems reduce productivity. Teams may miss updates, duplicate work, or make costly errors.
- Education: Students without internet access or proper devices struggle to participate in online learning. Teachers may face difficulty sharing materials or providing timely feedback.
- Healthcare: When health professionals can’t access or share electronic health records easily, patient safety is at risk. Delayed or misunderstood communication can have serious consequences for those with chronic conditions or in long-term care.
Across all sectors, overcoming technological barriers is essential for timely, inclusive, and high-quality communication.
Overcoming Technological Barriers to Communication
So, how can you overcome technological barriers in communication? The answer lies in a combination of planning, training, and investment in the right tools.
Upgrade Infrastructure
Reliable infrastructure is a must. Ensure high-speed internet access, modern routers, and up-to-date computer hardware are available for everyone who needs them. This investment supports the use of digital communication tools, especially for remote teams or online learning environments.
Choose Compatible and User-Friendly Tools
Select communication platforms and software that are compatible across devices and operating systems. Focus on user interface simplicity—look for clear layouts, accessible features, and good documentation. Avoid tools that require complex setups or are hard to integrate with existing systems.
Provide Training and Support
Education is key. Offer regular training sessions for staff, clients, or students to build confidence in using digital communication devices and platforms. Support channels, such as helpdesks or online tutorials, can make a big difference for those facing difficulties.
Address Security and Privacy Concerns
Implement strong, but not restrictive, security measures. Balance protection with ease of use. Make sure staff know how to handle sensitive information safely. Regularly audit systems to identify and address risks, especially in fields like healthcare, where privacy is critical.
Encourage Inclusive Communication
Use tools and platforms that support multiple languages, accessibility features, and alternative formats (such as text-to-speech). Design communication processes with diverse needs in mind—think about disability, age, and cultural differences.
Reduce Information Overload
Set guidelines for email and messaging. Prioritize important communication channels, and encourage clear, concise messages. Digital platforms should help, not overwhelm, users with information.
Monitor and Improve
Gather feedback from users about their experience with communication tools. Monitor key performance indicators, such as message delivery rates, meeting attendance, or workflow efficiency. Use this data to refine technology choices and training programs.
How Technology Can Also Bridge Gaps?
While it’s true that technology can be a barrier, it’s also a powerful way to foster inclusive communication and overcome traditional obstacles. Modern software applications allow people with disabilities to participate more fully in society. Video conferencing tools connect remote teams and family members, making communication possible across distances and time zones.
For the elderly, new devices and apps—when designed with accessibility in mind—support self-care and independent living. Information and communications technology helps organizations provide better long-term care, track chronic conditions, and keep everyone informed.
The key is to choose the right tools, maintain up-to-date infrastructure, and keep people at the heart of every decision.
Conclusion
Technological barriers to communication are a real challenge in today’s connected world. They can disrupt the flow of information, hinder effective communication, and lead to costly mistakes or misunderstandings in business, education, and healthcare. But these barriers are not impossible to overcome.
By investing in modern infrastructure, choosing user-friendly tools, offering ongoing training, and addressing privacy and accessibility, organizations and individuals can break down these barriers. Inclusive communication builds stronger teams, better learning environments, and safer healthcare systems.
If you want to improve the quality of communication in your organization or daily life, start by identifying the main technological obstacles and take practical steps to overcome them. Making communication accessible, secure, and efficient benefits everyone—no matter where they are or what challenges they face.




